Alternatives to bone grafting for dental implants have emerged as a promising solution to address bone defects caused by trauma, disease, or congenital conditions. These alternatives aim to reduce complications such as donor site morbidity, infection, and long recovery periods, offering safer and less invasive treatment options.
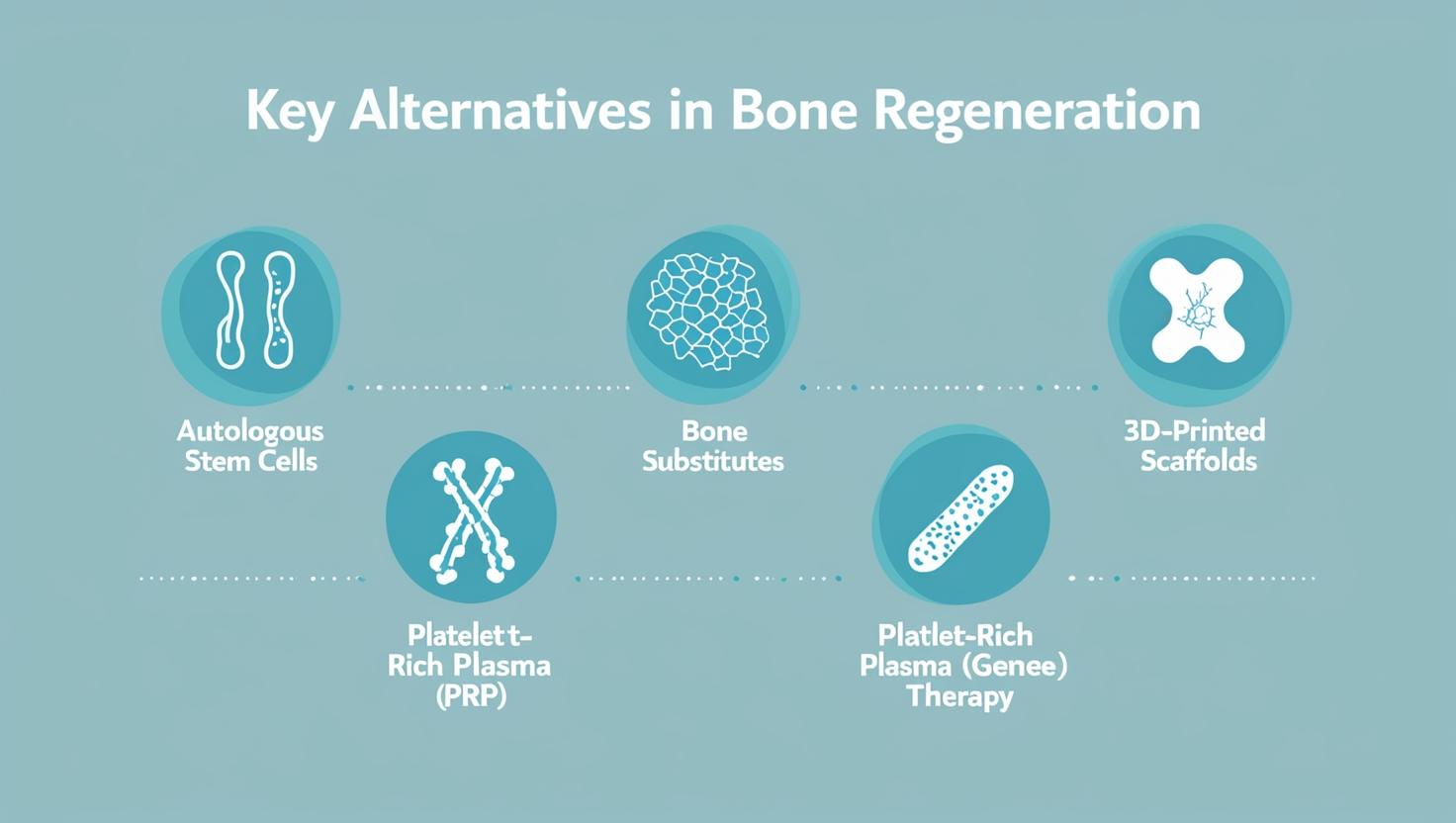
Key alternatives include autologous stem cells, bone substitutes, 3D-printed scaffolds, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and gene therapy. Each of these methods offers unique benefits in promoting bone healing and regeneration, but they also come with challenges, such as cost, availability, and varying patient responses. Research continues to improve these approaches.
What are the Alternatives to Bone Grafting?
Bone grafting has become an important role of reconstructive surgery for years. It has an importat effect in facilitating the healing of bone defects. These bone defects are generally resulted from trauma, disease, or congenital conditions.
Despite the fact that it is helpful, bone grafting has also many negative sides such as; complications related to donor site morbidity, infection, and long recovery periods. As a result, the medical field has seen significant improvements in alternate to bone graft for dental implants. It provides patients safety, efficiency, and less invasive treatment options.
In the following you can find the positive and negative sides of alternatives to bone grafting like the use of stem cells, bone substitutes, 3D-printed scaffolds, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and gene therapy.
Alternatives to Bone Grafting
With the help of today’s technology, there become some possible alternatives to bone grafting such as stem cells, bone substitutes, 3D-printed scaffolds, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and gene therapy. Let’s see them in details below;
| 1. Stem cells |
| 2. Bone Substitudes |
| 3. 3D-printed scaffolds |
| 4. PRP |
| 5. Gene Therapy |
1. Autologous Stem Cells
Stem cell therapy has gained attention as one of the alternatives to bone grafting so far. Autologous stem cells are derived from the patient’s own body. They ensure compatibility and reduce the risk of immune rejection.
These stem cells, often harvested from bone marrow or adipose tissue. They also can differentiate into various cell types like osteoblasts. These are responsible for bone formation. When applied to a bone defect, stem cells promote tissue regeneration and accelerate healing.
The advantages of using autologous stem cells are like that they harness the body’s own healing mechanisms and eliminate the need for external donor tissues. More, they can be associated with complications such as; rejection and transmission of disease.
However, there are some limitations. The limitations of this technique are like that the time required to culture and expand stem cells in the laboratory, as well as the potential for variability in patient response. Additionally, the procedure can be a bit expensive.

2. Bone Substitutes
Bone substitutes include synthetic materials, allografts which means it is donor’s bone and xenografts which means it is an animal bones. It represents one of the another alternatives to bone grafting.
These materials are used to fill bone defects and promote natural bone healing. Synthetic bone substitutes, such as hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate, behave like the mineral composition of natural bone. Also, it allows a better integration with the body’s native tissue.
Allografts and xenografts provide a more natural alternative. Because it is used real bone from human or animal sources. These materials can offer perfect structural support and promote osteogenesis on the other name bone formation.e
However, there are also som disadvantges such as; the risk of disease transmission, immune response, and poor integration in some cases. Despite these negative sides, bone substitutes are widely used. Because their availability, reduced surgical time, and ability to minimize donor site morbidity.

3. 3D-Printed Bone Scaffolds: Alternatives to Bone Grafting
3D printing technology has a revolution in many industries. And also, in the medical field. The capability of creating personalized bone scaffolds using a patient’s imaging data has opened up new possibilities for bone repair. These scaffolds are made from biocompatible materials that promote the growth of new bone tissue.
The most important positive side of 3D-printed bone scaffolds is their capability of being customized to the exact shape and size of the bone defect. This is particularly important in complex cases such as jaw or facial reconstruction.
The scaffolds are biodegradable which means they mostly dissolve as the natural bone heals. They reduce the need for additional another surgeries. Moreover, 3D printing provides a control over the structure of the scaffold that ensures optimal conditions for bone regeneration.
However, disadvantages such as high costs, limited availability, and the need for specialized equipment, reduce the widespread adoption of this technology. Despite these negative sides, 3D printing remains one of the alternatives to bone grafting, particularly in cases where customization is critical.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Growth Factors
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is another innovative approach to bone grafting. PRP involves extracting a patient’s own blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then reintroducing the PRP into the site of the bone defect.
Platelets contain growth factors that stimulate tissue repair and regeneration, promoting faster and more effective healing as alternatives to bone grafting. PRP therapy is minimally invasive and leverages the body’s natural healing properties. It makes it an attractive option for patients who wish to avoid surgery.
While PRP has been shown to accelerate healing in various soft tissues, its efficacy in bone regeneration is still under research. Moreover, PRP may not be suitable for large or complex bone defects, and results can vary from patient to patient.
5. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy represents one of the other alternatives to bone grafting. This technique involves the delivery of specific genes to the site of the bone defect to stimulate the production of proteins that promote bone growth.
For example, genes that code for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) can be introduced to the affected area to encourage healing. These are naturally occurring in the body and play a key role in bone formation. Gene therapy has the potential to offer a more permanent solution to bone defects with the help of long-term bone regeneration.
However, it is still in the experimental phase and faces several circumstances such as; safety, the delivery of genes to the target site, and the long-term effects of such treatments. Nonetheless, gene therapy holds great promise for the future, particularly as research progresses and techniques improve.
What are the Alternatives to Bone Grafting?
To sum up, the evolution of bone grafting techniques leeds to the development of a variety of alternatives to bone grafting. The aim of these alternatives is to reduce the risks and complications associated with traditional bone grafting.
Autologous stem cells, bone substitutes, 3D-printed scaffolds, PRP, and gene therapy all provides unique advantages and challenges for alternatives to bone grafting. While these alternatives are not yet universally applicable, they offer hope for more personalized, effective, and less invasive treatments in the future.
The researches continue to advance for alternatives to bone grafting. It is likely that these methods will play an increasingly significant role in bone repair and regeneration, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the advantages of alternatives to bone grafting?
This is the most asked FAQ in the field. It provides patients safety, efficiency, and less invasive treatment options.
What are the disadvantages of alternatives to bone grafting?
Bone grafting has also many negative sides such as; complications related to donor site morbidity, infection, and long recovery periods. However, the aim of these alternatives is to reduce the risks and complications associated with traditional bone grafting.
How many alternatives are there for bone grafting in our day?
There are 5 alternatives to bone grafting such as; stem cells, bone substitutes, 3D-printed scaffolds, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and gene therapy.
Is stem cells technique costly?
As this technique requires time to culture and expand stem cells in the laboratory, as well as the potential for variability in patient response. So, the procedure can be a bit costly.